Une thérapie optimale pour de meilleurs soins aux patients et de meilleurs résultats
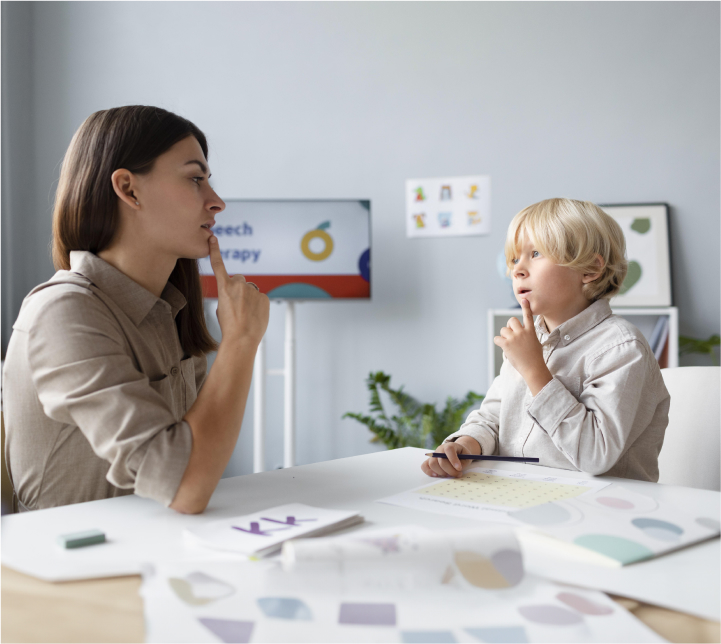

Une thérapie optimale pour de meilleurs soins aux patients et de meilleurs résultats
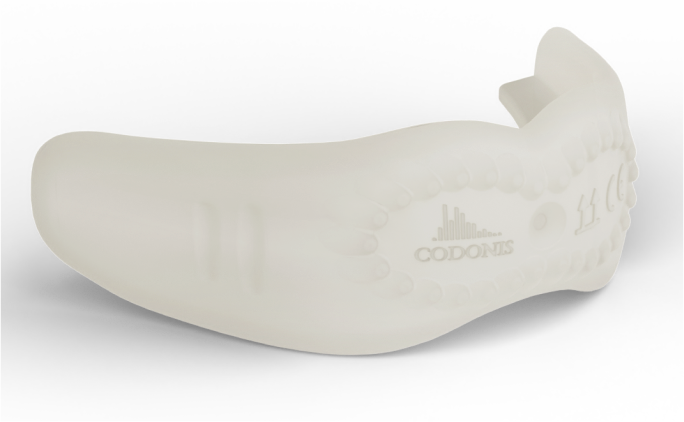

Pour tous les âges
Le CODONIS LWZ est conçu de manière unique pour s’adapter aux enfants en dentition primaire jusqu’aux personnes âgées.
Conception de surface unique
Le CODONIS LWZ dispose d’une surface nodulaire unique pour stimuler les structures musculaires adjacentes
Positionnement
Pour maintenir le CODONIS LWZ en place, l'appareil est équipé de tampons d’occlusion.
CODONIS App
Plate-forme unique pour la personnalisation de CODONIS LWZ avec le plan de thérapie
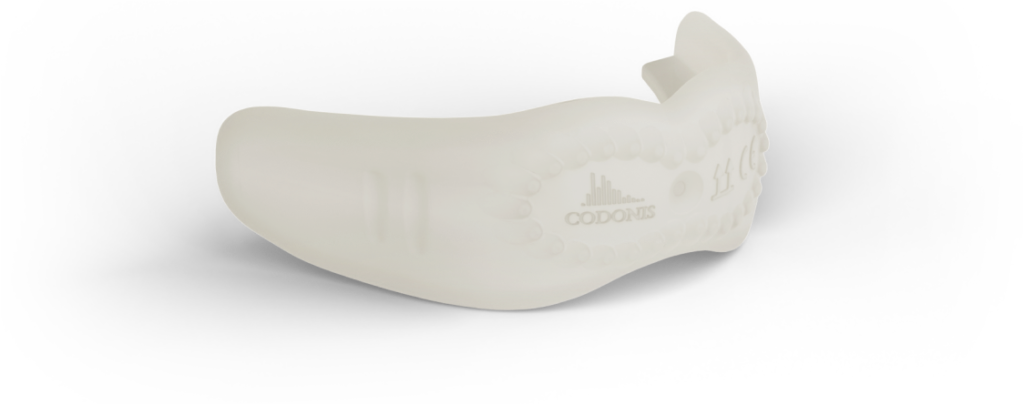
Le CODONIS LWZ dispose d’une surface nodulaire unique pour stimuler les structures musculaires adjacentes
Le CODONIS LWZ est conçu de manière unique pour s’adapter aux enfants en dentition primaire jusqu’aux personnes âgées.
Pour maintenir le CODONIS LWZ en place, l'appareil est équipé de tampons d’occlusion.
Plate-forme unique pour la personnalisation de CODONIS LWZ avec le plan de thérapie
Au cours de la phase de familiarisation, la durée de l’utilisation de l’appareil est régulièrement augmentée
Pendant la phase intensive, le thérapeute encourage le patient à utiliser CODONIS LWZ pendant une durée prolongée.
Au cours de la phase descendante, les durées de traitement sont régulièrement réduites.
Des contrôles de stabilisation sont proposés afin de s’assurer qu’il n’y aura pas de récidives, en général, après 1 mois, 3 mois et 6 mois depuis le dernier usage.
Facile – en quelques étapes, le CODONIS LWZ est commandé


Ahmad, M. and Schiffman, E.L. (2016) ‘Temporomandibular Joint Disorders and Orofacial Pain’, Dental clinics of North America, 60(1), pp. 105–124. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cden.2015.08.004
D’Onofrio, L. (2019) ‘Oral dysfunction as a cause of malocclusion’, Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research, 22 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), pp. 43–48. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.12277
Grabowski, R., Kundt, G. and Stahl, F. (2007) ‘Interrelation between occlusal findings and orofacial myofunctional status in primary and mixed dentition: Part III: Interrelation between malocclusions and orofacial dysfunctions’, Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics = Fortschritte Der Kieferorthopadie: Organ/Official Journal Deutsche Gesellschaft Fur Kieferorthopadie, 68(6), pp. 462–476. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00056-007-0717-y
Huber, Bettina (2017) Wirkungsweise des Lippen-Wangen-Zungen-Trainers (LWZ-Trainers) auf das infantile Schluckmuster (Pilotstudie). Master Thesis. Klinik für Mund -, Kiefer- und Gesichtschirurgie Universitätsspital Basel.
Koka, V. et al. (2021) ‘Orofacial Myofunctional Therapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Pathophysiological Perspective’, Medicina, 57(4), p. 323. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57040323
Pizolato, R.A., Freitas-Fernandes, F.S. de and Gavião, M.B.D. (2013) ‘Anxiety/depression and orofacial myofacial disorders as factors associated with TMD in children’, Brazilian Oral Research, 27(2), pp. 156–162. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1806-83242013000100021
Ray, J. (2006) ‘Orofacial myofunctional deficits in elderly individuals’, The International Journal of Orofacial Myology: Official Publication of the International Association of Orofacial Myology, 32, pp. 22–31.
Seemann, J., Kundt, G. and Stahl de Castrillon, F. (2011) ‘Relationship between occlusal findings and orofacial myofunctional status in primary and mixed dentition: part IV: interrelation between space conditions and orofacial dysfunctions’, Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics = Fortschritte Der Kieferorthopadie: Organ/Official Journal Deutsche Gesellschaft Fur Kieferorthopadie, 72(1), pp. 21–32. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00056-010-0004-1
Streff, Susanne (2017) Evaluation der Wirkweise des Lippen-Wangen-Zungen-Trainers auf die orofaziale Muskulatureine prospektive Pilotstudie bei Erwachsenen aus logopädischer Sicht. Master Thesis. Klinik für Mund-, Kiefer- und Gesichtschirurgie Universitätsspital Basel.
Sude, A. et al. (2021) ‘Temporomandibular Disorder Related Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Oromandibular Dystonia Patients in Two Different Clinical Settings: A Cross-Sectional Study’, Journal of oral rehabilitation, 48(5), pp. 542–550. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.13162
Nous recommandons d’utiliser le CODONIS LWZ pour un cycle standard d’environ 3 mois. Après cette période, le CODONIS LWZ doit être remplacé.
Le CODONIS LWZ peut être utilisé partout où se trouve le patient. Pour des raisons d’hygiène, le patient doit s’assurer qu’il se nettoie les mains avant d’utiliser l’appareil.
Oui, c’est possible.
Cela dépend du patient et de sa capacité à utiliser le CODONIS LWZ. Il peut être conseillé d’adapter d’abord l’appareil aux enfants ou à la personne en situation de handicap, puis d’effectuer la thérapie selon le plan de routine.
CODONIS is a Swiss based company which develops and markets innovative and forward-looking medical products for logopedics, myofunctional therapy and dentistry.
Office:
Tramstrasse 99, 4132 Muttenz, Switzerland
Email:
contact@codonis.ch
VAT: CHE-316.119.424
Ahmad, M. and Schiffman, E.L. (2016) ‘Temporomandibular Joint Disorders and Orofacial Pain’, Dental clinics of North America, 60(1), pp. 105–124. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
D’Onofrio, L. (2019) ‘Oral dysfunction as a cause of malocclusion’, Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research, 22 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), pp. 43–48. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/ocr.
Grabowski, R., Kundt, G. and Stahl, F. (2007) ‘Interrelation between occlusal findings and orofacial myofunctional status in primary and mixed dentition: Part III: Interrelation between malocclusions and orofacial dysfunctions’, Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics = Fortschritte Der Kieferorthopadie: Organ/Official Journal Deutsche Gesellschaft Fur Kieferorthopadie, 68(6), pp. 462–476. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/
Huber, Bettina (2017) Wirkungsweise des Lippen-Wangen-Zungen-Trainers (LWZ-Trainers) auf das infantile Schluckmuster (Pilotstudie). Master Thesis. Klinik für Mund -, Kiefer- und Gesichtschirurgie Universitätsspital Basel
Koka, V. et al. (2021) ‘Orofacial Myofunctional Therapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Pathophysiological Perspective’, Medicina, 57(4), p. 323. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/
Pizolato, R.A., Freitas-Fernandes, F.S. de and Gavião, M.B.D. (2013) ‘Anxiety/depression and orofacial myofacial disorders as factors associated with TMD in children’, Brazilian Oral Research, 27(2), pp. 156–162. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1806-
Ray, J. (2006) ‘Orofacial myofunctional deficits in elderly individuals’, The International Journal of Orofacial Myology: Official Publication of the International Association of Orofacial Myology, 32, pp. 22–31.
Seemann, J., Kundt, G. and Stahl de Castrillon, F. (2011) ‘Relationship between occlusal findings and orofacial myofunctional status in primary and mixed dentition: part IV: interrelation between space conditions and orofacial dysfunctions’, Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics = Fortschritte Der Kieferorthopadie: Organ/Official Journal Deutsche Gesellschaft Fur Kieferorthopadie, 72(1), pp. 21–32. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/
Streff, Susanne (2017) Evaluation der Wirkweise des Lippen-Wangen-Zungen-Trainers auf die orofaziale Muskulatureine prospektive Pilotstudie bei Erwachsenen aus logopädischer Sicht. Master Thesis. Klinik für Mund-, Kiefer- und Gesichtschirurgie Universitätsspital Basel.
Sude, A. et al. (2021) ‘Temporomandibular Disorder Related Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes in Oromandibular Dystonia Patients in Two Different Clinical Settings: A Cross-Sectional Study’, Journal of oral rehabilitation, 48(5), pp. 542–550. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.
Réservez votre place pour notre formation en ligne !